The latest tweets from @magicentoplugin. Magento Open Source delivers features to build and grow a unique online store from the ground up. However, if you need an all-in-one cloud solution that is optimized, easy to deploy, provides enhanced security, and is packed with additional integrated capabilities to accelerate sales; consider Magento.
The following guide refers to a standard Magento maintenance mode page. If you need to use a custom maintenance page, see Create the custom maintenance page topic.
Magento uses maintenance mode to disable bootstrapping. Disabling bootstrapping is helpful while you are maintaining, upgrading, or reconfiguring your site.
Magicento
Magento detects maintenance mode as follows:
- If
var/.maintenance.flagdoes not exist, maintenance mode is off and Magento operates normally. Otherwise, maintenance mode is on unless
var/.maintenance.ipexists.var/.maintenance.ipcan contain a list of IP addresses. If an entry point is accessed using HTTP and the client IP address corresponds to one of the entries in that list, then maintenance mode is off.
Log in as file system owner
To log in as the file system owner:
Log in to the Magento server as, or switch to, a user with permissions to write to the Magento file system. See switch to the Magento file system owner.
If you use the bash shell, you can use the following syntax to switch to the Magento file system owner and enter the command at the same time:
If the Magento file system owner does not allow logins, you can do the following:
To run Magento commands from any directory, add
<magento_root>/binto your systemPATH.Because shells have differing syntax, consult a reference like unix.stackexchange.com.
Sample bash shell for CentOS:
Optionally, you can run the commands in the following ways:
cd <magento_root>/binand run them as./magento <command name><magento_root>/bin/magento <command name><magento_root>is a subdirectory of your web server docroot.
In addition to the command arguments discussed here, see Common arguments.
Install Magento
Before you use this command to enable or disable maintenance mode, you must install the Magento software.
Enable or disable maintenance mode
Use the magento maintenance CLI command to enable or disable Magento maintenance mode.
Command usage:
--ip=<ip address> is an IP address to exempt from maintenance mode (for example, developers doing the maintenance). To exempt more than one IP address in the same command, use the option multiple times.
Using --ip=<ip address> with magento maintenance:disable saves the list of IPs for later use. To clear the list of exempt IPs, use magento maintenance:enable --ip=none or see Maintain the list of exempt IP addresses.
magento maintenance:status displays the current status of maintenance mode.
For example, to enable maintenance mode with no IP address exemptions:
To enable maintenance mode for all clients except 192.0.2.10 and 192.0.2.11:
After you place Magento in maintenance mode, you must stop all message queue consumer processes.One way to find these processes is to run the ps -ef | grep queue:consumers:start command, and then run the kill <process_id> command for each consumer. In a multiple node environment, repeat this task on each node.
Maintain the list of exempt IP addresses
To maintain the list of exempt IP addresses, you can either use the [--ip=<ip list>] option in the preceding commands or you can use the following:
<ip address> .. <ip address> is an optional space-delimited list of IP addresses to exempt.
--none clears the list.
Multi-store setups
Magento Logo
If you want to set up multiple stores, each with a different layout and localized content, pass the $_GET['skin'] parameter to the intended processor.In the following example, we are using a 503 type error template file, which requires localized content.
The constructor of the Error_Processor class accepts a skin GET parameter to change the layout:

This can also be added to a rewrite rule in the .htaccess file that will append a skin parameter to the URL.
$_GET[‘skin’] parameter
To use the skin parameter:
- Check if the
.maintenance.flagexists. - Note the host address, that refers to the
HTTP_HOST, or any other variable such as ENV variables. - Check if the
skinparameter exists. Set the parameter by using the rewrite rules below.
Here are some examples of rewrite rules:
- RewriteCond
%{DOCUMENT_ROOT}/var/.maintenance.flag -f - RewriteCond
%{HTTP_HOST} ^sub.example.com$ - RewriteCond
%{QUERY_STRING} !(^|&)skin=sub(&|$)[NC] - RewriteRule
^ %{REQUEST_URI}?skin=sub[L]
- RewriteCond
Copy the following files:
pub/errors/default/503.phtmltopub/errors/sub/503.phtmlpub/errors/default/css/styles.csstopub/errors/sub/styles.css
Edit these files to provide localized content in the
503.phtmlfile and custom styling in thestyles.cssfile.Ensure your paths point to your
errorsdirectory. The directory name must match the URL parameter indicated in theRewriteRule. In the previous example, thesubdirectory is used, which is specified as a parameter in theRewriteRule(skin=sub)
The nginx setting must be added for multi-store setups.
Skip to end of metadataGo to start of metadataMagicento
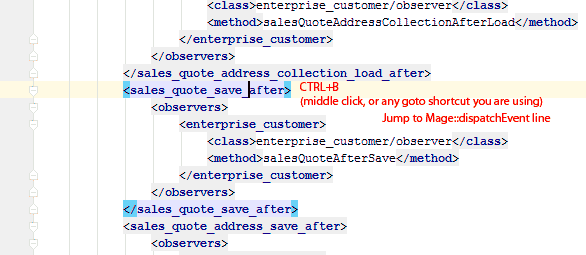
Magicento is a free PHPStorm plugin for Magento developers.

Features include: Goto for factories and template paths, autocomplete for factories, xml files and class names, documentation for xml nodes, evaluation of PHP code inside Magento environment, and much more to come!
YiiStorm
YiiStorm is a plugin for PhpStorm IDE that is adding code navigation enhancements for Yii framework based projects.
Features are: Going from render and renderPartial to the view file. Includes controllers, partials and widgets. Supports all ways of specifying a view: themes, smarty .tpl views and external actions; Going from model name in relations() to the model class; Going from the $this->widget('path.to.widget.Class') call to the widget class; Going from controller actions() to action class.
Symfony2 - Clickable Views
Symfony2 - Clickable Views is a plugin for Symfony2 Framework developers. Resolves on CTRL+Click the corresponding twig template in your Symfony2 project. This plugin demands a projectstructure which you can find in the Symfony2 Std. Edition and will not work with custom layouts.
Magento Ecommerce
Symfony2 - Factory Support
Magicento
Symfony2 - Clickable Views is a plugin for Symfony2 Framework developers. Resolves on CTRL+Click the corresponding twig template in your Symfony2 project. This plugin demands a projectstructure which you can find in the Symfony2 Std. Edition and will not work with custom layouts.
